

This is because some of the differentiated tumour cells regain the ability to generate new CSCs upon CSC ablation ( Batlle and Clevers, 2017). An additional challenge for the efficient elimination of CSCs is the enhanced plasticity of CSCs when compared with adult stem cells. However, this approach faces similar challenges to studies of adult stem cell biology, namely significant heterogeneity between tumours and within the tumour, and a lack of unique markers of quiescence or dormancy to allow for targeted therapies. Therapies targeting quiescent adult stem cells and niche elements are therefore currently being developed and tested. In line with this, it was noted that disseminated tumour cells that acquired a dormant state are responsible for metastases that appear many years after primary tumour treatment ( Giancotti, 2013 Linde et al., 2016 Sosa et al., 2014). This observation prompted the hypothesis of the existence of cancer stem cells (CSCs) and suggested that quiescence contributes to the ability of tumours to relapse after treatment ( Batlle and Clevers, 2017 Nassar and Blanpain, 2016 Schillert et al., 2013 Sutherland and Visvader, 2015).
#Somatic stem cells definition full
Similarly, tumours often efficiently regenerate their full heterogeneity after radiotherapy or chemotherapy, which targets mostly proliferating cells. Quiescent adult stem cells resist environmental or radiation-induced stress and can regenerate their whole lineage after an insult ( Der Vartanian et al., 2019 Doetsch et al., 1999 Scaramozza et al., 2019).
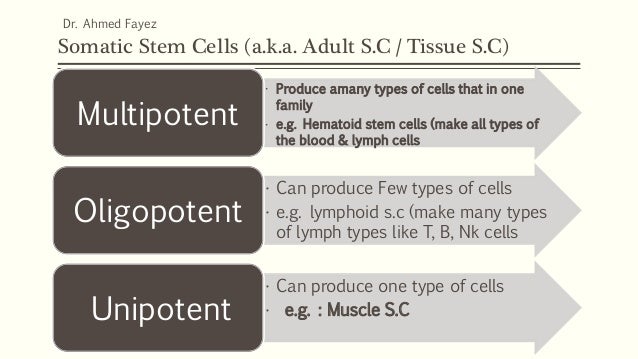
Quiescent stem cells also exist in numerous cancer types, and they contribute to the ability of tumours to evade radiotherapy and chemotherapy ( Box 1). In contrast, insufficient quiescence can lead to the formation of tumours or, when stem cell activation is not linked to self-renewal, to exhaustion of the stem cell pool. Excessive quiescence can lead to the generation of too few proliferative cells to cope with the homeostatic needs of tissues ( Cheung and Rando, 2013). Quiescence is essential for the long-term maintenance of adult stem cells and tissue functions. The blood is one high turnover ‘tissue’ that is exempt from this generalization hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) remain mostly quiescent and give rise to multipotent progenitors to sustain blood cell production during normal homeostasis ( Crane et al., 2017 Nakamura-Ishizu et al., 2014 Pinho and Frenette, 2019).
#Somatic stem cells definition skin
Indeed, adult stem cells that exist in a quiescent state can be found in many tissues, but the proportion of quiescent adult stem cells appears to be more prevalent in low turnover tissues, such as skeletal muscle or brain, when compared with rapidly renewing tissues, such as the skin or the gut ( Clevers and Watt, 2018). One such strategy is to remain in a non-proliferative state, called quiescence, which is thought to protect the DNA of cells from mutations acquired during successive rounds of cell division ( Walter et al., 2015). Adult stem cells in different tissues use various strategies to ensure their maintenance over the lifespan of the organism ( Mohammad et al., 2019).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
